This lesson talks about food chains and food webs in our environment.
A food chain is a flow of energy from a green plant (producer) to an animal (consumer) and to another animal (another consumer) and so on. In this lesson we are going to talk all about food chains and food webs in the environment.
All organisms need energy to live. Energy is obtained from food. Green plants are the only organisms that can capture energy from sunlight and make their own food.
Try Food Chains Quiz 1 and Food Chains Quiz 2 at the end of the lesson to check your knowledge about food chains and food webs.
A green plant should always be the first link of a food chain. Green plants are the only organisms that can directly get the sun’s energy and make their own food through a process called photosynthesis.
Herbivores are animals that only feed on plants.
Omnivores are animals that eat a variety of food of both plant and animal origin.
Carnivores are animals that only feed on other animals.
Carnivores are also known as the top predators as they are at the highest point of the food chain. Top predators have a little or no enemies. They usually consume all lower levels and are not consumed by any other animals until they die.
Lions, tigers, crocodiles, eagles are the best examples of top predators.
Prey is an animal that a predator feeds on. For example, a lion feeds on a zebra. So, the zebra is the prey of the lion.
All animals depend on plants directly or indirectly for food and energy.
Primary consumers are the second link of a food chain. They are usually herbivores that eat green plants or sometime omnivores that eat both plants and animals.
Let’s look at some types of food chain in the examples below.
The green plants are the food of all herbivores that are primary consumers.
Secondary consumers are the third link of a food chain. They can be either omnivores or carnivores.
The herbivores are the food for carnivores that are secondary, tertiary or quaternary consumers.
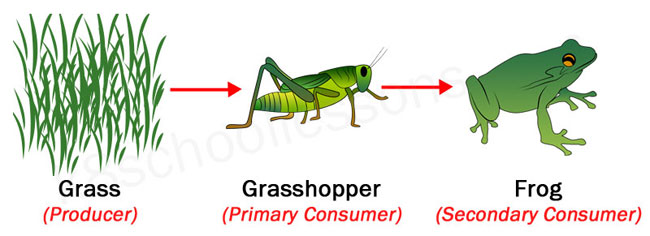
Example of a food chain with three links showing the producer, the primary consumer and the secondary consumer
Tertiary consumers are the fourth link of a food chain while quaternary consumers are the fifth link of a food chain. They are usually the carnivores that are top predators.
Secondary consumers are the food for carnivores or top predators that are tertiary or quaternary consumers.
Sometimes tertiary consumers can be the food for quaternary consumers.
Likewise, step by step, the energy in food flows from the producers to consumers.
When an organism dies, it is eventually eaten by scavengers and broken down by decomposers like bacteria and fungi, and the exchange of energy continues in the environment.
Crows, vultures and hyenas are the best examples of vertebrate scavengers while ants are good invertebrate scavengers in the environment. They eat dead bodies of animals and plants.
Bacteria, fungi, algae, lichens are the best examples of decomposers. They break down dead bodies of plants and animals and let the essential nutrients in the dead matter mix with the ecosystem again, so that no waste would pile up.
A food chain is a flow of energy from a green plant (producer) to an animal (consumer) and to another animal (another consumer) and so on.
Each of these organisms in a food chain is called a link. These links make a food chain.
This is the link where energy from the sun enters the food chain.
In nature the food chains are not as direct as we’ve seen them in our discussion. The food chains are highly cross linked (connected) and highly complicated. In any habitat there may be many kinds of animals that feed on the same plants and there may be many predators that feed on the same kinds of prey. Therefore there will be several food chains in any habitat. These food chains are inter-linked and they form food networks in the habitat.
A food web is a type of a food network with several inter-linked food chains in a habitat.