Human brain is the main control center of your body, in fact it is in charge of your entire body. Human brain consists of three main parts; cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem. This lesson, human brain for kids, teaches more facts about the human brain.
Functions of the human brain:
Your brain needs lots of energy to do all these. Therefore, it needs a good supply of oxygen. This helps you to think, have ideas, feel emotions, change moods, express desires, solve problems, and store and recall memories. These are known as higher mental processes.
Also, part of your automatic brain is involved in involuntary actions, such as controlling heartbeat, breathing, digestion etc., without your knowledge. These are known as lower-level processes. Your autonomic nervous system (ANS) deals with these body processes.
The human brain is an organ made of dense, greyish-pink tissue. It feels like stiff jelly and is covered with deep wrinkle-like grooves. The human brain is composed of neurons, blood vessels and some supporting cells called glia. The brain has got its greyish colour from the neurons and pink colour from the blood vessels.
An average adult human brain weighs about 1400 g and contains billions of neurons and trillions of glial cells. These help you to think, feel, remember, dream, control your body and live.
Make fists with both of your hands and put them together. Now you can get a rough idea of how big your brain is.
Did you know?
There can be about as many cells in your brain as there are stars in the galaxy or the Milky Way!
Your brain has got an amazing protection as it is the most vital part in your body.
The human brain is located inside the head. It is protected by the bones of the skull and a covering of three thin membranes called meninges. For extra protection the brain is surrounded and cushioned by liquid that helps to absorb shocks.
The human brain has its main parts. At this stage we are going to learn the following major parts of the human brain.
The cerebrum is the large, wrinkled lump that curves over, and covers most of the other parts of the human brain. It makes up about 85 percent of the weight of the brain. The surface of the cerebrum is folded, so that it has a large surface area. We call this area cerebral cortex.
The cerebrum is the ‘thinking part’ of the human brain. Different areas of the cerebrum are in charge of different activities.
Functions of the cerebrum:
The cerebrum is divided vertically into two halves. They are;
The cerebral hemispheres look similar. The halves are connected by bundles of nerve fibres. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes, or regions. Both hemispheres are the control centers for different skills and abilities.
Functions of the left cerebral hemisphere:
Example:
Hand movements and the control of speech of a right-handed person come from the left cerebral hemisphere.
(a) learning and using language
(b) numbers and math
(c) reasoning and logic problems
Functions of the right cerebral hemisphere:
Example:
Hand movements and the control of speech of a left-handed person come from the right cerebral hemisphere.
(a) general ideas and concepts
(b) overall shape, colours and forms, recognition of things we see, such as quickly recognizing a face
(c) art and music awareness
(d) Intuition, and jumping to an idea or conclusion
(e) judging distance and position (spatial awareness)
 Functions of the left and right halves of the human brain
Functions of the left and right halves of the human brain
The left side of the human brain picks out details, while the right side sees and understands the whole idea. Both sides work together and help each other.
This is the outer layer of the cerebrum. This is a large and thick surface area folded into bulges and grooves.
The cerebral cortex consists of different areas that deal with different parts of the body and various parts of our thinking or mental processes.
Human brain can help humans to;
The other important part of the human brain is the cerebellum. The cerebellum lies at the rear lowermost part of the brain, at the back of the brainstem.
We can stand up straight, walk, lean, bend, and jog with almost no conscious thought, because of the cerebellum.
Functions of the cerebellum:
How does the cerebellum coordinate posture, balance and movement?
The cerebellum also checks movements as they happen, and fine-tunes them with small adjustments. If a drastic problem takes place, the cerebellum sends signals back to the cortex, in order to make us think to deal with the problem.
This is the stalk for the whole brain, which connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord. Medulla is one of the main parts of the brainstem.
Medulla controls most of your body’s involuntary actions.
Functions of the Medulla:
Examples:
(a) Watching how the ball moves at a game of tennis
(b) Watching the racing cars of a car race
All these are vital body processes. If the brainstem becomes inactive due to any damage, there is less or no hope for recovery. This is called ‘brainstem inactivity’ or ‘brain death’.
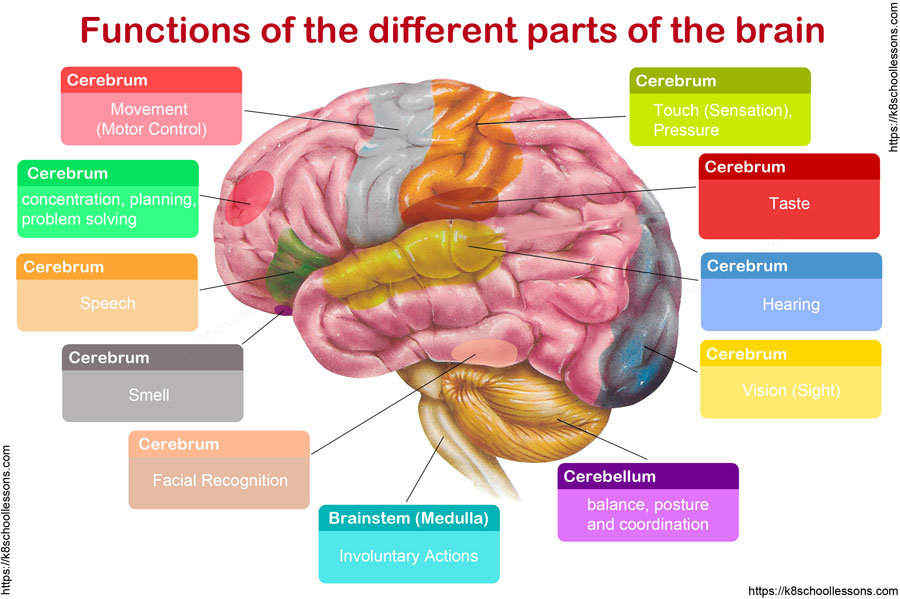 Functions of the different parts of the Human Brain
Functions of the different parts of the Human Brain
How do you learn and remember things?
You create connections between cells in your brain when you learn to do something. Next time you do it, the connections are already there, so that it is easier to carry out what you are doing. This is what we call memory and how we remember things.
What is memory?
The amazing ability that your brain has got to store information and then use it when needed is called memory.
Your memory plays a very important part in learning and intelligence. No matter how simple or complex the task is, you need your memory to carry it out.
Your short-term memory only holds information for about a minute. You use it to compare prices when you go shopping, or to remember a name when you meet someone new.
How good are you at remembering your name, your parents’, siblings’, friends’ and teachers’ names?
You know all these names by heart. Also, you remember your parents’ phone numbers and some important phone numbers very well.
Then what about a skill such as riding a bike???
You do not have to learn to ride a bike everyday like you do not have to learn to walk everyday.
Some names, phone numbers and many skills can be kept for many years in your long-term memory.
Like your memory, your brain controls your emotions too. This is why memories of things that happened a long time ago can still make you emotional.
These are kinds of emotions that we feel every day.
While we all feel these emotions in our minds, our bodies show them too.
We like to live in groups. We enjoy our loved ones company. We laugh together. We joke together. We enjoy sharing our experiences with each other. This helps us to feel closer to each other. Sharing bad experiences with others makes us feel better when we are sad.
Fear is a useful emotion. It helps the body stay away from things that could harm it.
What are phobias?
Phobias are fears of things, such as spiders, cockroaches that you do not really need to be afraid of.
Your brain is still very busy, although you feel that it switches off when you sleep. We need to have a good sleep after a busy day. Adequate sleep relaxes you and makes you feel better, giving you a healthy lifestyle.
While you sleep, electrical activity in the brain, known as brain waves, changes. It seems that the brain uses that time to sort out information it received while you were awake.
Do we grow while we sleep?
Yes, you do grow while you sleep. There is a small gland at the base of the human brain, called the pituitary gland. It releases lots of a chemical signal, called a growth hormone while you sleep. This hormone makes you grow. So it is very important to get a good night’s rest.
How much sleep do we need?
The amount of sleep that one should need varies according to the different age groups. Newborn babies sleep on and off all day, for 16 hours or more. After gradually getting into a routine, and once children are at school they just sleep through the night. Adults need much less sleep than children. Look at the chart below.
Age group | Amount of sleep needed |
Birth to 1 year | 16 hours or more |
2 to 8 years | 10 to 13 hours |
9 to 13 years | 9 to 11 hours |
14 to 17 years | 8 to 10 hours |
17+ years | 7 to 9 hours |
Napping
Some like to nap during the day too, whereas some prefer only to sleep at night. A short nap can help to restore energy levels and make you feel refreshed.
Dreaming
Do you dream while you sleep? Then you may want to know how you dream during sleep.
Your brain goes in and out of a type of sleep during sleep. We call this Rapid Eye Movement or REM. At this stage, although your body stops moving, your eyes flicker and flit about. During REM sleep we do most of our dreaming.
Sleepwalking
Sometimes people get up and move around in sleep at night.
For example;
The person may simply sit up and look around, or do more complex things such as get dressed or even eat food.
This is called sleepwalking. No one knows why sleepwalking happens.
Sleepwalking is quite common, especially in young children.
Hope you’ve enjoyed learning the facts about the human brain with our lesson, Human Brain for Kids.