We all have seen trees full of fruits. Oranges, apples, peaches, nectarines, grapes are all plants that bear fruits. But, have you ever thought of how these plants produce fruits.
In this lesson we are going to learn about how pollination and fertilization take place in flowers in order to produce fruits.
At the end of the lesson you can go to the Quiz on Pollination and Fertilization and check your knowledge on the lesson.
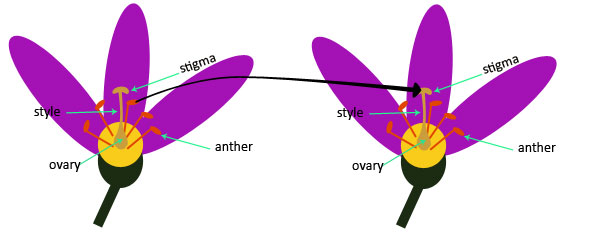
Pollination is the transfer (move) of pollen grains from the anther (of the stamen) to the stigma (of the pistil).

How pollination takes place between pollen grains and stigma of two different flowers of same species
1) Between pollen grains and stigma of the same flower.
2) Between pollen grains and stigma of different flowers of same species.
Pollen grains are very light in weight, so they can easily float in the air and move to other plants.
1. All flowers don’t have brightly coloured petals.
2. Some grasses have small, dull, off-white flowers.
3. This is because they are not pollinated by insects or other animals.
4. They use the wind to blow their pollen grains to other plants.

Plants with flowers that get pollinated by wind
When it is raining, pollen grains can be washed away and brought to the stigma.
Animals like insects, birds and squirrels can transfer pollen grain to other flowers.
When insects like bees go from one flower to another, pollen grains in one flower can be stuck in their body parts and brought to the stigma of another flower.

A bee gathering nectar from a flower
After a flower is pollinated, each pollen grain which is on the stigma grows a tiny tube towards the ovules in the ovary. Then the male sex cells in pollen grains can reach the ovules and join female sex cells or eggs produced in ovules. This makes the female sex cells or eggs fertilize. This joining or the combination of male sex cells and female sex cells in a flower is what we call fertilization. Fertilization cannot take place without pollination.
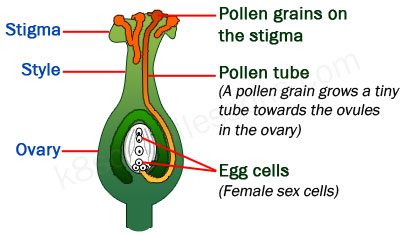
How fertilization takes place in flowers
After fertilization the petals, the stamen and the stigma fall off. The ovules become the seeds. The ovary becomes the fruit.

Changes after the fertilization of a butternut pumpkin flower

The butternut pumpkin flower’s ovary has turned into a complete fruit and its petals, stamen and stigma have fallen off