The four main parts of a flower include the carpel, stamen, petals and sepals. The carpel consists of three parts; stigma, style and ovary. The stamen contains the anther and filament. There are also several other parts of a flower such as receptacle, nectary, peduncle (stalk), pedicel, and perianth.
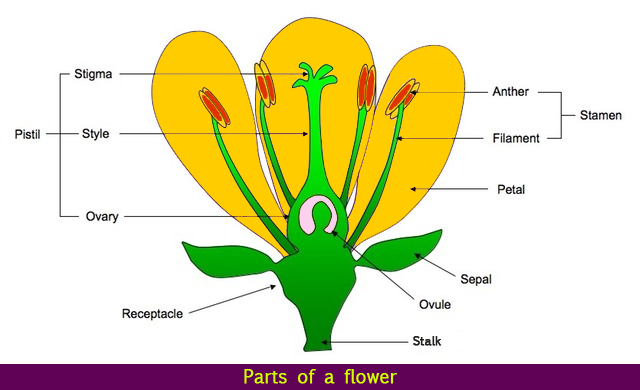
All these parts of a flower collectively create the anatomy of a flower.
Flowers are a vital part of our ecosystem. The main objective of a flower is sexual reproduction. Reproduction helps plants to spread their species in the environment and make sure the survival of their species. All the parts of a flower work together to help them grow, reproduce, attract pollinators and fruit. They provide food for pollinators like bees and butterflies, which in turn pollinate plants, enabling them to reproduce. So, without flowers, many plant species would not be able to survive, and the entire ecosystem would be affected. By knowing the anatomy of a flower and the functions of each part of a flower, we can understand their role in the ecosystem and appreciate the beauty and complexity of flowers and their importance in our world.
Flowers come in all shapes, sizes, and colors and different from one another. However, the basic anatomy of all flowers has several parts in common. There are four main parts of a flower which make a flower a complete flower. There are some flowers which do not have these main four parts. So, they are considered incomplete flowers.
The carpel and the stamen are the reproductive parts of a flower, the female organ and the male organ respectively. These two parts work together and produce seeds. This process is the sexual reproduction in plants and it takes place in flowers.
If a flower has both the carpel and the stamen we call it a perfect flower so, it is a bisexual flower. But also remember, not all perfect flowers have all the four main key parts of a flower.
Some flowers have either the carpel or the stamen. So, we call them imperfect flowers or unisexual flowers.
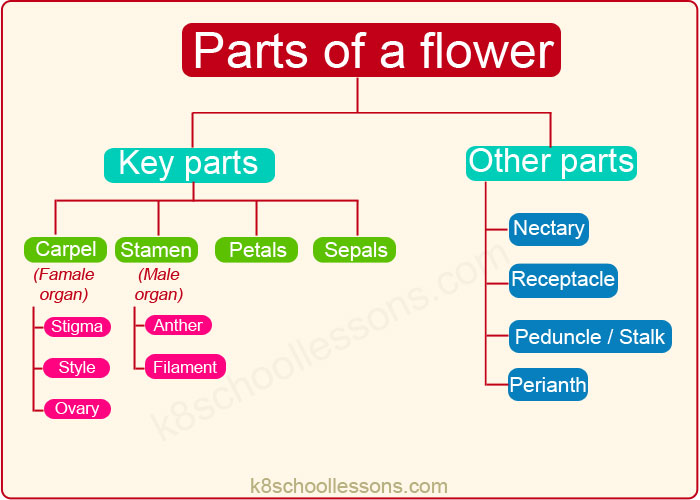 Parts of a Flower Chart
Parts of a Flower Chart
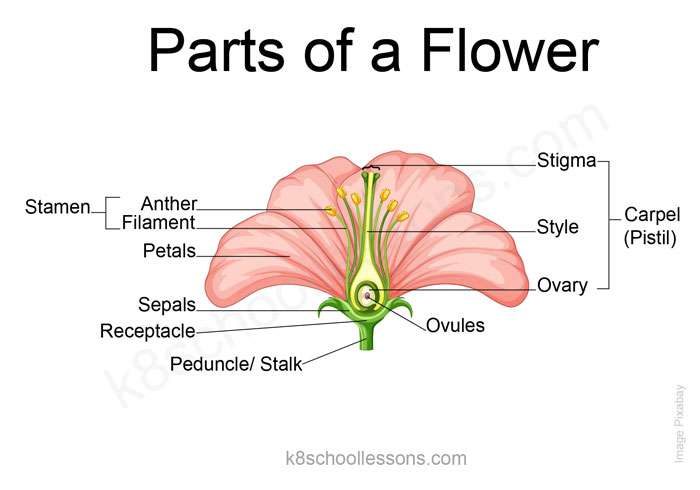 Parts of a Flower
Parts of a Flower
Now, let’s learn about each of these parts in detail.
Carpel is the female reproductive part of a flower. It is also called the pistil. Carpel consists of three main parts.
The stigma contains a sticky substance. Its job is to catch the pollen grains. These pollen grains can stick to stigma.
The style is the stalk like thing that holds up the stigma.
Ovary holds ovules or eggs. Ovules produce female sex cells.
After fertilization the ovules become the seeds. The ovary becomes the fruit. (Click to read the lesson ‘Pollination and Fertilization‘)
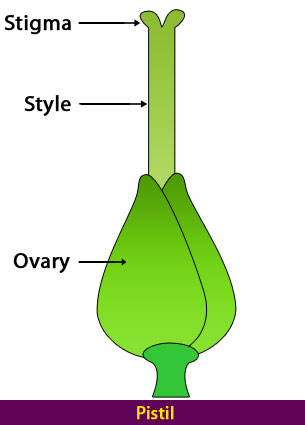 Carpel or Pistil of a Flower
Carpel or Pistil of a Flower
Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower. Stamen consists of two main parts.
Anther holds a yellow dust called pollen grains. Each pollen grain has a male sex cell.
Filament holds up the anther.
 Stamens of a natural flower
Stamens of a natural flower
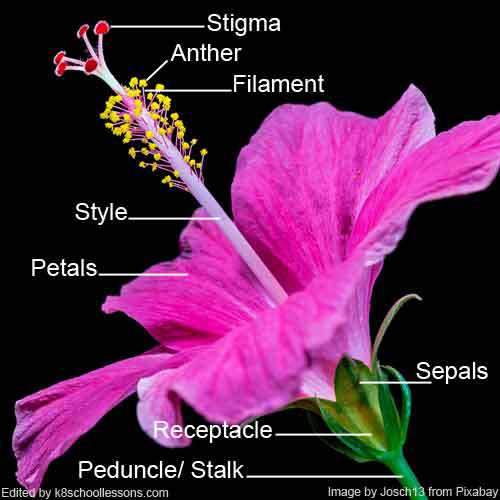 Parts of a natural flower
Parts of a natural flower
Petals are often very brightly coloured. The main job or function of petals is to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies for pollination. The bright colors and sweet fragrances of the petals help to lure in these insects, which then transfer pollen from one flower to another.
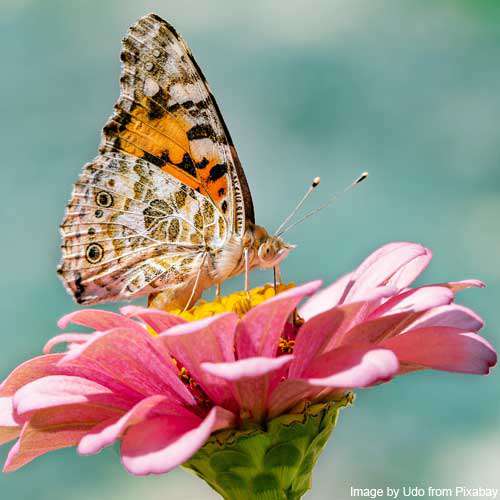 The main job of petals is to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies for pollination.
The main job of petals is to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies for pollination.
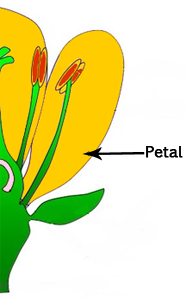 Petal
Petal
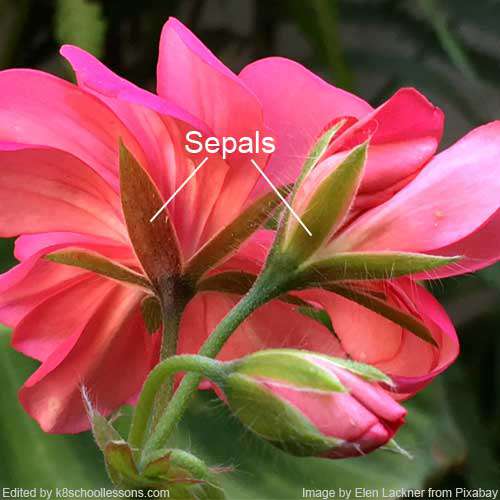
Sepals are special types of leaves that form a ring around the petals. Their job is to protect the flower while it is still a bud. Sepals help to protect the developing flower from damage and pests before it blooms. After the flower has opened, the sepals can still be seen behind the petals. Sepals are usually green or brown, although in some plants they are the same colour as the petals.
Even after the flower transforms into a fruit, the sepals of some fruits remain visible.

 Sepals of some fruits remain visible, even after the flower transforms into a fruit.
Sepals of some fruits remain visible, even after the flower transforms into a fruit.
Bract can be mistakenly identified as petals in certain flowers such as bougainvillea and poinsettia. In plants that lack sepals, a bract serves a similar function as a sepal. It is a modified leaf that appears more petal-like than leaf-like, with distinct coloring and shape compared to other leaves on the plant.
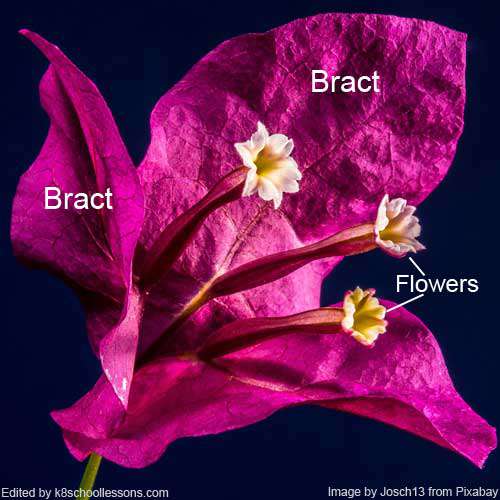 Bracts of bougainvillea
Bracts of bougainvillea
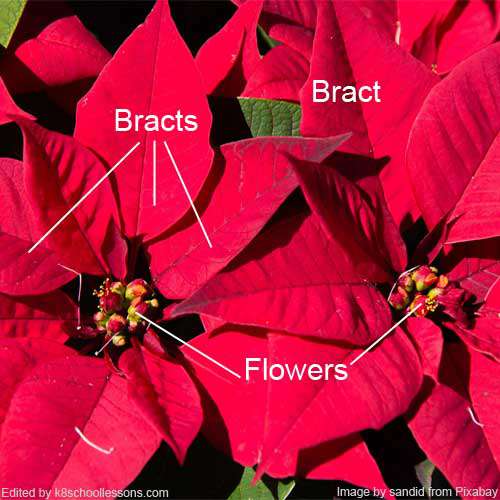 Bracts of poinsettia
Bracts of poinsettia
All the petals of a flower together are called the corolla.
 Corolla
Corolla
All the sepals of a flower collectively known as the calyx.
 Calyx
Calyx
The nectary makes nectar in the flower. Nectar is a sweet substance, which insects drink to give them energy. Bees also use nectar to make honey. The nectary is usually right in the centre of the flower. This means the insects have to reach deep into the flower to find the nectar. As they do so, their bodies pick up pollen from the anthers, and they carry it to the next flower they visit.
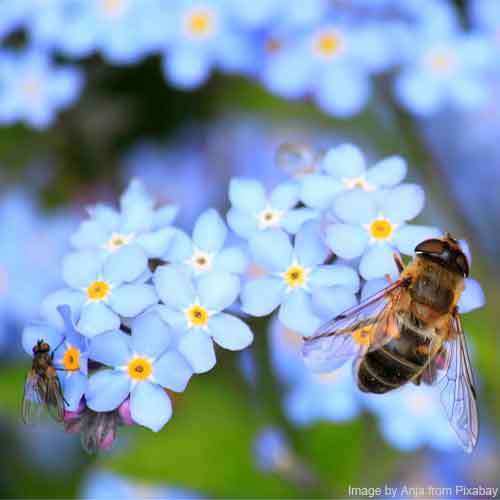 Bees use nectar to make honey
Bees use nectar to make honey
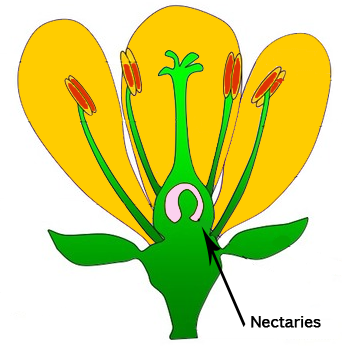 Nectary
Nectary
The receptacle is the uppermost part of the flower stalk to which all flower parts are attached. The receptacle is usually large and rounded in shape, because its main function is to support the weight of the flower or the developing fruit.
 Receptacle
Receptacle
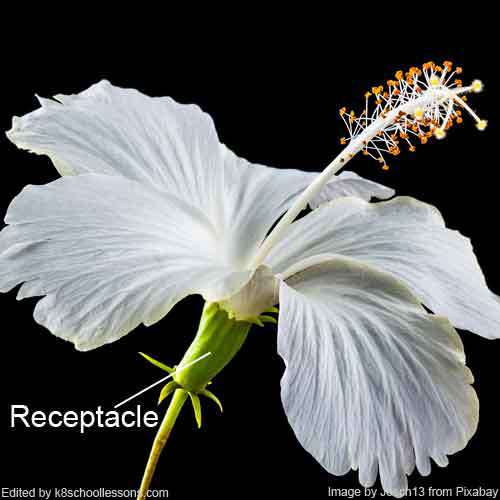 Receptacle
Receptacle
The peduncle is the stalk that provides support for the flower and later the fruit.
 Peduncle / stalk
Peduncle / stalk
A pedicel is a secondary stalk that branches off the main stem, and from which flowers grow. Pedicels are typically found in plants that produce inflorescences, such as clusters or similar arrangements.
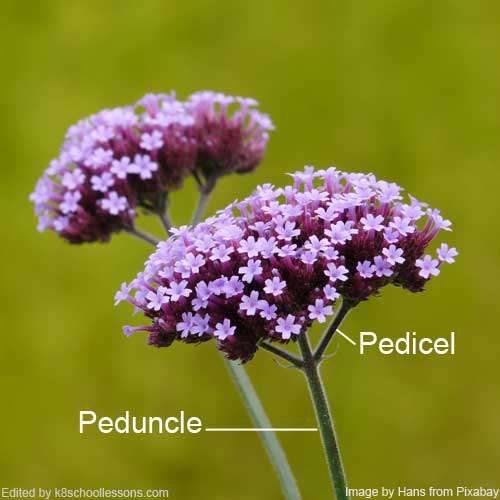 Pedicel
Pedicel
Corolla and calyx together are called the perianth.
 Perianth
Perianth
There are two types of reproduction in plants.
Asexual reproduction in plants refers to the process of producing new plants from vegetative structures, such as leaves, stems, or roots, without the involvement of gametes or fertilization. Therefore, flowers are not involved in asexual reproduction and takes place in non-flowering plants. Non-flowering plants do not bear flowers.
This type of reproduction can occur naturally or can be induced through human intervention, such as by taking cuttings or using tissue culture. Asexual reproduction in plants allows for the efficient propagation of desirable traits and is widely used in horticulture and agriculture. It also enables plants to reproduce quickly and efficiently in environments where sexual reproduction may not be feasible.
Sexual reproduction in plants is the process by which male and female gametes (reproductive cells) combine to produce a new individual that has a unique genetic makeup different from both parents. This process involves the fusion of male and female gametes, which can occur either within the same flower (self-pollination) or between different flowers (cross-pollination). Therefore, flowers are involved in sexual reproduction and takes place in flowering plants.
Sexual reproduction in plants is essential for genetic diversity and enables the development of new traits that may enhance the survival and adaptation of the species. It also allows for the formation of seeds and fruits, which are important for the dispersal of offspring and the propagation of the species.